iPSC Culture: What Every Researcher Needs to Know
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have become a mainstay in disease modeling and drug development, offering almost unlimited opportunities to study human biology in the lab. However, working...
Cell of the Month – Kupffer Cells
Welcome back to our Cell of the Month series! This time, we are talking about Kupffer cells - what they are, what they do, and why we should want to learn more about them! Kupffer cells - the...
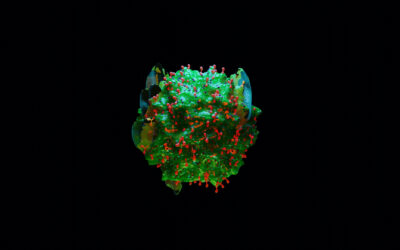
Cell of the Month: Mast Cells
Mast cells are tissue-resident immune cells derived from the myeloid lineage, and along with basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils, they belong to the granulocyte family of white blood cells. ...
Cell of the Month: Pericytes
It’s a fibroblast-like cell adorned with long cytoplasmic processes that wrap around the endothelial cells in blood vessels, it controls blood flow through the blood vessels, and it is essential for...
CRISPR Screen Identifies Potential New Regulators of Fibrosis in Human Liver Cells
In our last few liver articles, we highlighted the urgent need for new models and treatments for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and looked at the potential for human liver organoids to not...
Human Liver Organoids as a New Model for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
The lack of approved treatments for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatosis (NASH) is largely explained by the shortcomings of cellular models used to unravel disease...
Cell of the Month: Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) are highly specialized liver endothelial cells that form a physical barrier between the blood and hepatocytes. They are the most abundant non-parenchymal...
NASH – The Urgent Need for Better Disease Models and New Therapies
This article was originally published on 4th April 2023. It was revised and republished on 19th March 2023, to reflect important updates in the NASH therapeutic development space, including FDA...
Cell of the Month: Cells in a 3D Spheroid
Spheroids have been used in cell culture for decades. In the 1980s, different types of human cancer cells --normally grown as monolayers or suspension cultures--were tested for their innate...